New conditions and syndromes often emerge, generating both excitement and skepticism. One such topic that has gained traction is Leaky Brain Syndrome—a condition some claim is responsible for neurological dysfunction, mental health disorders, and chronic inflammation. But is leaky brain a real, medically recognized condition, or is it just another buzzword fueled by alternative health trends?
To answer this, we must first understand the intricate system that protects our brain—the blood-brain barrier (BBB)—and explore the science behind its potential dysfunction.
The Blood-Brain Barrier: Your Brain’s Defense System
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective membrane that acts as a protective shield between the bloodstream and the brain. It prevents harmful substances, pathogens, and toxins from entering the central nervous system while allowing essential nutrients and oxygen to pass through.
This barrier is composed of endothelial cells, which are tightly packed together, forming a nearly impenetrable wall. These cells are supported by astrocytes and pericytes, which regulate permeability and maintain the barrier’s integrity.
A healthy blood-brain barrier ensures that neurons function optimally and are protected from inflammatory responses. However, when this barrier becomes compromised, it may allow unwanted substances to leak into the brain, triggering neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and even neurological disorders.
What Causes a “Leaky Brain”?
The term “leaky brain” is used to describe a state where the blood-brain barrier becomes permeable, allowing toxins, bacteria, and inflammatory molecules to pass through. This phenomenon has been observed in scientific research, particularly in conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis (MS), traumatic brain injury, and chronic stress. Several factors are believed to contribute to increased permeability of the blood-brain barrier:
1. Chronic Inflammation
Inflammation is one of the primary culprits in breaking down the blood-brain barrier. Conditions like autoimmune disorders, chronic infections, and prolonged stress can trigger an inflammatory response, damaging the integrity of the BBB.
2. Gut-Brain Axis Dysfunction
A growing body of research suggests a strong connection between gut health and brain health. A condition known as leaky gut syndrome—where the intestinal lining becomes overly permeable—has been linked to increased permeability of the blood-brain barrier. When toxins and bacteria from the gut enter the bloodstream, they can provoke an immune response that affects the brain.
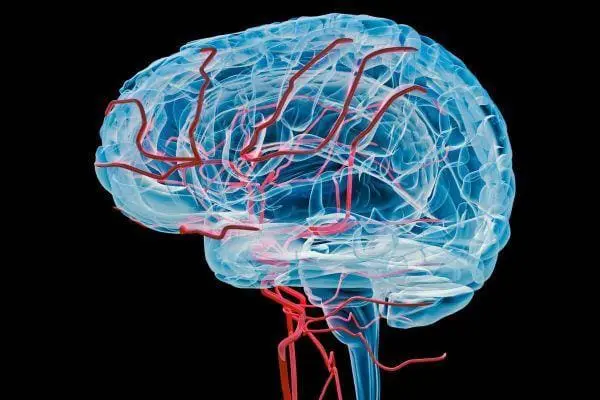
3. Chronic Stress and Cortisol Overload
Prolonged exposure to stress and high levels of cortisol can weaken the blood-brain barrier. Studies indicate that stress-related inflammation may degrade the BBB, allowing neurotoxins and inflammatory agents to infiltrate the brain.
4. Toxin Exposure and Environmental Factors
Heavy metals (such as lead and mercury), air pollution, pesticides, and chemical additives in food have been shown to damage the blood-brain barrier over time. Additionally, excessive alcohol consumption and drug use can also compromise BBB integrity.
5. Poor Diet and Nutrient Deficiencies
A diet high in processed foods, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats contributes to systemic inflammation, which in turn weakens the blood-brain barrier. On the other hand, deficiencies in essential nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and antioxidants can impair BBB function.
Leaky Brain and Its Potential Health Effects
If the blood-brain barrier becomes too permeable, harmful substances may enter the brain, leading to various neurological and cognitive symptoms. Some researchers believe leaky brain syndrome could be linked to:
1. Cognitive Decline and Neurodegenerative Diseases
A compromised blood-brain barrier has been observed in Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis (MS). These conditions are often accompanied by chronic inflammation and the accumulation of harmful proteins in the brain.
2. Brain Fog and Mental Fatigue
Many people who claim to experience leaky brain report symptoms like difficulty concentrating, poor memory, and mental sluggishness. While these symptoms are not exclusive to leaky brain, they may be a sign of chronic neuroinflammation.
3. Mood Disorders and Mental Health Issues
Emerging research suggests that a weakened blood-brain barrier may play a role in depression, anxiety, and even schizophrenia. When inflammatory molecules enter the brain, they can disrupt neurotransmitter balance, affecting mood and emotional regulation.
4. Autoimmune Neurological Conditions
Certain autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis, involve the immune system attacking the nervous system. Some scientists believe that a leaky blood-brain barrier could contribute to the development of autoimmune reactions in the brain.
Scientific Evidence: Is Leaky Brain a Recognized Medical Condition?
While the concept of blood-brain barrier dysfunction is well-documented in neurology and medical research, the term “leaky brain syndrome” is not officially recognized by major medical institutions like the World Health Organization (WHO) or the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
However, studies have confirmed that the BBB can become compromised under certain conditions. For example:
- A 2018 study published in Nature Neuroscience found that a breakdown in the blood-brain barrier is associated with cognitive decline in aging.
- Research in the Journal of Neuroinflammation (2020) highlights how systemic inflammation contributes to BBB dysfunction, potentially playing a role in depression and neurodegenerative diseases.
- Studies on Alzheimer’s patients reveal that disruptions in the blood-brain barrier may allow harmful proteins, such as beta-amyloid plaques, to accumulate in the brain.
These findings suggest that while leaky brain syndrome itself may not be a formally recognized diagnosis, the mechanisms behind it are real and worth further investigation.
How to Protect and Strengthen the Blood-Brain Barrier
While there is no official medical treatment for “leaky brain syndrome”, many strategies can help support blood-brain barrier integrity and brain health.
1. Reduce Inflammation Through Diet
A whole-food, anti-inflammatory diet can be beneficial for brain health. Foods rich in antioxidants, polyphenols, and healthy fats can help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation.
- Eat more: Leafy greens, berries, turmeric, wild-caught fish (high in omega-3s), nuts, seeds, and fermented foods.
- Avoid: Processed foods, refined sugars, trans fats, and artificial additives.
2. Support Gut Health
A healthy gut microbiome is essential for a strong blood-brain barrier. Prebiotic and probiotic foods can improve gut integrity and reduce systemic inflammation.
- Probiotic-rich foods: Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi.
- Prebiotic foods: Garlic, onions, bananas, asparagus.
3. Manage Stress Effectively
Since chronic stress can degrade the BBB, incorporating stress-management techniques is crucial. Meditation, breathwork, and yoga can lower stress hormones. Adequate sleep is essential for BBB repair and detoxification.
4. Detoxify from Environmental Toxins
Limiting exposure to harmful chemicals can help protect brain health. Use organic produce to avoid pesticides. Choose glass over plastic to reduce exposure to endocrine disruptors. Install air and water filters to reduce environmental toxins.
5. Optimize Key Nutrients
Certain nutrients help strengthen the blood-brain barrier and protect against neuroinflammation.
- Omega-3 fatty acids (DHA & EPA) – Found in fish and flaxseeds.
- Vitamin D – Supports immune regulation and brain function.
- Curcumin (from turmeric) – A powerful anti-inflammatory compound.
By incorporating these lifestyle and dietary changes, it is possible to promote a healthy blood-brain barrier, reduce inflammation, and enhance cognitive function.